As a YouTube creator, understanding copyright laws is crucial to avoid legal issues and protect your work. This guide covers:
-
Copyright Basics: Copyright gives creators exclusive rights over their original work, protecting various forms of creative expression like videos, music, images, and written content.
-
YouTube's Copyright Rules: YouTube has rules to protect creators' work and ensure users follow copyright laws, including:
- Content ID System to detect copyrighted content
- Copyright claims vs. strikes for violations
- Fair use guidelines for limited use of copyrighted material
-
Using Copyrighted Content: You can legally use copyrighted content with:
- Permission from the copyright holder
- Fair use for commentary, criticism, news reporting, teaching, etc.
- Licensed or royalty-free content
-
Avoiding Copyright Issues: Best practices include:
- Using your own original content
- Obtaining licenses and permissions
- Understanding fair use provisions
- Using royalty-free resources
-
Handling Claims and Strikes: If you receive a claim or strike, you can dispute it, submit a counter-notification, or retract the strike.
-
Copyright and Monetization: To use copyrighted content in monetized videos, you need permission, licenses, or fair use provisions.
-
Copyright Resources: Learn about copyright from YouTube's Copyright Center, Copyright School, and other resources. Manage your content with tools like Content ID and Copyright Match Tool.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure your content is original, properly licensed, or used within fair use provisions, allowing you to maintain a successful YouTube channel while respecting intellectual property rights.
Related video from YouTube
Copyright Basics
What is Copyright?
Copyright is a legal right that gives the creator of an original work control over how it is used, distributed, and monetized. It protects various forms of creative expression, including written works, music, art, and more.
Types of Protected Works
Copyright protection covers different types of works, such as:
| Type of Work | Examples |
|---|---|
| Literary works | Novels, blogs, poems, articles |
| Musical works | Songs, musical notes |
| Dramatic works | Plays |
| Choreographic works | Dance routines, band routines |
| Visual works | Photographs, paintings, drawings, sculptures |
| Audiovisual works | Movies, commercials |
| Sound recordings | Audiobooks, sound effects |
| Architectural works | Building plans |
Copyright Ownership and Duration
The creator of the original work typically owns the copyright. However, copyright ownership can sometimes be transferred to another party through agreements or contracts.
The duration of copyright protection varies, but it generally lasts for a certain number of years after the creator's death or from the date of publication.
Public Domain and Fair Use
1. Public Domain
Works in the public domain are no longer protected by copyright law, meaning anyone can use them freely.
Works can enter the public domain through:
- Copyright expiration
- The creator's explicit waiver
2. Fair Use
Fair use is a legal exception that allows specific uses of copyrighted material under certain conditions, such as:
- Commentary
- Criticism
- News reporting
- Teaching
- Scholarship
- Research
While both public domain and fair use involve using copyrighted material, they are different concepts.
YouTube's Copyright Rules
YouTube has rules to protect creators' work and ensure users follow copyright laws. Understanding these rules is important to avoid copyright issues and keep your channel safe.
Content ID System
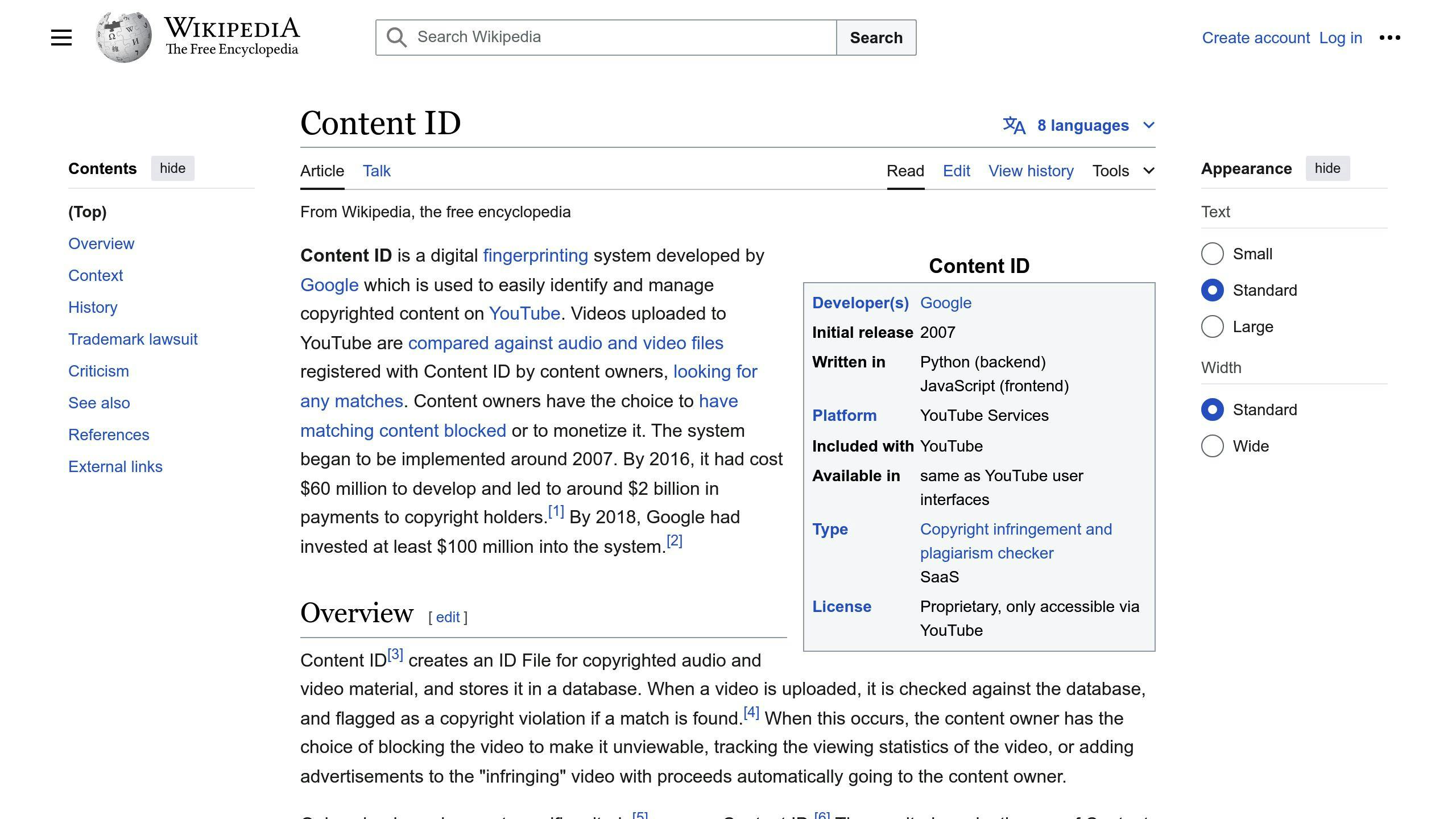
YouTube's Content ID system automatically detects and manages copyrighted content on the platform. It uses technology to identify audio and video files that match copyrighted material in its database. When a match is found, the copyright owner can choose to:
- Monetize the content (earn money from it)
- Track the content (see where it's being used)
- Block the content (remove it from YouTube)
Claims vs. Strikes
A copyright claim is a notification sent to you when your content is identified as using someone else's copyrighted work. You can resolve claims by:
- Removing the content
- Providing proof of ownership
- Disputing the claim
A copyright strike is a formal notice from YouTube for violating their copyright policy. Strikes can lead to:
- Content removal
- Suspension of monetization
- Channel termination
| Number of Strikes | Consequence |
|---|---|
| 1st strike | Content removal, warning |
| 2nd strike (within 90 days) | Monetization and live streaming suspended for 2 weeks |
| 3rd strike (within 90 days) | Channel termination |
Fair Use Guidelines
YouTube's fair use guidelines allow creators to use copyrighted material without permission in certain cases, such as:
- Criticism
- Commentary
- News reporting
- Teaching
- Scholarship
- Research
Fair use is complex, and you must ensure your use of copyrighted material falls under these categories without infringing on the copyright owner's rights.
Using Copyrighted Content
Creating content for YouTube involves understanding when and how you can legally use copyrighted material. Here are the scenarios where using copyrighted content is allowed:
Legal Use
- Fair Use: You can use copyrighted material without permission for criticism, commentary, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, or research purposes.
- Permission from Copyright Holder: If you obtain permission from the copyright holder, you can legally use their content.
- Public Domain: Works in the public domain are not protected by copyright, and you can freely use them.
Getting Permission
To obtain permission to use copyrighted material, follow these steps:
- Identify the Copyright Holder: Find out who owns the copyright to the material you want to use.
- Contact the Copyright Holder: Reach out and ask for permission to use their material.
- Provide Context: Explain how you plan to use the material.
- Wait for a Response: The copyright holder will respond with a yes or no, or may request more information.
Licensed or Royalty-Free Content
Using licensed or royalty-free content is a convenient and legal way to access copyrighted material. Here are the benefits:
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fair Use | Using content for commentary, criticism, etc. | No cost, legal protection | Risk of disputes, unclear rules |
| Licensing | Obtaining permission from the copyright holder | Legal clarity, higher quality content | Cost, time-consuming |
| Royalty-Free | Using content from libraries offering royalty-free licenses | Easy to use, low cost | Limited selection |
Best Practices
To legally use copyrighted content on YouTube, follow these best practices:
- Understand Fair Use: Make sure you understand the rules and guidelines for fair use.
- Get Permission: Always obtain permission from the copyright holder when possible.
- Use Licensed or Royalty-Free Content: Consider using licensed or royalty-free content for convenience and legal clarity.
- Give Credit: Always give credit to the original creator of the content, even if you have permission to use it.
Avoiding Copyright Issues
Use Your Own Original Content
The best way to avoid copyright problems is to create your own original content. By making your own music, images, and videos, you own the rights and can use them freely. This also lets you express your unique style and stand out from others.
Use Royalty-Free Resources
If creating original content isn't possible, use royalty-free resources. YouTube's Audio Library offers free, high-quality music and sound effects. Stock libraries like Unsplash, Pexels, and Pixabay provide royalty-free images and videos.
Get Licenses and Permissions
When using copyrighted material, get licenses and permissions. Find the copyright holder and ask for permission. Explain how you'll use the material and respect their intellectual property rights.
Understand Fair Use
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission. Consider these factors to determine if your use qualifies as fair use:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose and character | Is it for commentary, criticism, news reporting, teaching, research, or other transformative purpose? |
| Nature of the work | Is the original work factual or creative? |
| Amount used | How much of the original work is used? |
| Effect on the market | Does it impact the potential market for the original work? |
Fair Use Examples on YouTube
Fair use examples on YouTube include:
- Critiquing or reviewing a movie or TV show using short clips
- Creating a parody or satire of a copyrighted work
- Using copyrighted material for educational or research purposes
sbb-itb-bc761f5
Handling Claims and Strikes
Sometimes, you may receive a copyright claim or strike on YouTube. Here's how to handle them:
Claims and Strikes Explained
- Claim: A notification from a copyright owner that your video contains their copyrighted material.
- Strike: A penalty applied to your channel or video for using copyrighted material without permission or a license.
Responding to Claims and Strikes
If you receive a claim or strike, you have three options:
-
Dispute the claim
- If you believe the claim is invalid or your use falls under fair use, you can dispute it.
- Provide evidence to support your case.
-
Submit a counter-notification
- If you believe the strike was issued by mistake, submit a counter-notification.
- Provide your identification, contact information, and a statement that the material was removed due to an error.
-
Retract the strike
- If you acknowledge using copyrighted material without permission, retract the strike.
- Ensure you have the necessary permissions or licenses for future use.
Resolving Disputes
To resolve disputes successfully:
-
Communicate with the copyright owner
- Explain your side and provide evidence of fair use or permission.
- They may retract the claim or strike.
-
Provide evidence
- Gather proof of permission, licenses, or examples of fair use.
-
Follow YouTube's guidelines
- Understand and follow YouTube's copyright policies to avoid future issues.
| Dispute Resolution Steps |
|---|
| 1. Communicate with the copyright owner |
| 2. Provide evidence of fair use or permission |
| 3. Follow YouTube's copyright guidelines |
Copyright and Monetization
Copyright issues can severely impact your ability to earn money from your YouTube videos. This section explains the consequences of copyright violations on monetization and how to legally use copyrighted content in monetized videos.
Monetization Impact
If you receive a copyright claim or strike, it can prevent you from making money from your videos. In serious cases, repeated copyright infringement can lead to YouTube terminating your account. Even accidental use of copyrighted material can result in lost revenue and damage your reputation.
Using Copyrighted Content for Monetization
To legally use copyrighted content in monetized videos, you need permission from the copyright owner or use royalty-free content. You can do this through:
- Licensing agreements: Negotiate with the copyright owner to obtain a license to use their content.
- Royalty-free content: Use content that is explicitly licensed for use without royalties or permissions.
- Fair use: Use copyrighted content under fair use provisions, such as criticism, commentary, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, or research.
Monetization Options
Using licensed or royalty-free content can provide a safer and more reliable way to monetize your videos. Some benefits include:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced copyright risk | Minimize the risk of copyright claims and strikes. |
| Increased revenue | Focus on creating engaging content without worrying about copyright issues. |
| Improved reputation | Establish a reputation for respecting copyright laws and creators' rights. |
Copyright Resources
Learning About Copyright
YouTube provides helpful resources to understand copyright laws and avoid infringement:
- The YouTube Copyright Center explains copyright, fair use, public domain, and infringement.
- Copyright School covers copyright basics, fair use, and responding to claims.
Other sites with copyright information:
Managing Your Content
YouTube offers tools to manage and protect your content:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Content ID | Scans videos for copyrighted material, allowing owners to choose actions |
| Copyright Match Tool | Identifies and removes copyrighted content from your videos |
Legal Assistance
For complex copyright issues, consider legal consulting services:
A qualified attorney can provide expert advice on copyright laws and regulations, helping you navigate legal matters and avoid potential infringement.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
In summary, following YouTube's copyright rules and guidelines is essential for creators to avoid legal issues and maintain a successful channel. By implementing these best practices, you can ensure your content is original, properly licensed, or used within fair use provisions.
Remember:
- Respect the intellectual property rights of others.
- Use your own original content or obtain necessary licenses and permissions.
- Understand and correctly apply fair use provisions.
- Regularly monitor your content and promptly respond to claims and strikes.
- Stay informed about copyright laws and regulations.
| Best Practices |
|---|
| Use original content |
| Obtain licenses and permissions |
| Apply fair use provisions correctly |
| Monitor content and respond to claims/strikes |
| Stay updated on copyright laws |
FAQs
Can you use 10 seconds of a copyrighted video on YouTube?
No, you cannot use any part of a copyrighted video on YouTube without permission, even if it's just 10 seconds. It's a common misunderstanding that using a short clip is okay, but that's incorrect. Unless you get explicit permission from the copyright owner, you cannot use their content, regardless of the length.
Additionally, giving credit to the creator does not give you permission to use their copyrighted material. You must obtain clear permission or use royalty-free content to avoid copyright claims and strikes on YouTube.
| Using Copyrighted Content | Allowed? |
|---|---|
| Using 10 seconds without permission | No |
| Using any length without permission | No |
| Giving credit to the creator | No |
| Obtaining explicit permission | Yes |
| Using royalty-free content | Yes |



